Hello Melinda,
The thing is that there are 2 attributes in AD to identify when an account logged last time: Last Logon (LDAP name lastLogon) and Last-Logon-Timestamp (LDAP name lastLogonTimestamp). The Last Logon attribute was introduced in Windows 2000 Server, and Last-Logon-Timestamp was introduced a bit later, in Windows Server 2003. There are 2 differences between the attributes:
- Last Logon is not replicated, while Last-Logon-Timestamp is. This means that if you have multiple Domain Controllers (DCs) in your environment, on each DC the value of the Last Logon attribute will be different for the same account. On each DC, the value of the attribute will indicate the last time date/time when an account logged on to that particular DC.
- Last Logon is updated each time a user logs on, while Last-Logon-Timestamp is not. Active Directory uses a special algorithm to determine whether to update the value of the Last-Logon-Timestamp attribute or not.
For more information, have a look at the following articles on MSDN:
Also, if you want to perform some sort of cleanup in your AD, we suggest using the built-in Inactive User Deleter and Inactive Computer Deleter Scheduled Tasks. The tasks allow you to delete inactive users/computers from Active Directory on a certain periodic basis. For information on how to configure the deletion of inactive accounts, see the following tutorial: http://www.adaxes.com/tutorials_Automat ... ectory.htm.
Both the tasks use the If is inactive condition. The condition allows you to check whether a user or computer account is inactive for a certain period of time.
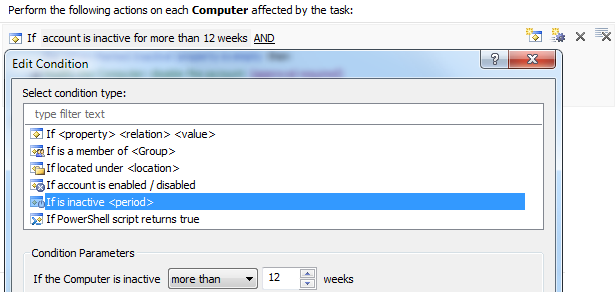
To determine for how long an account is inactive, Adaxes compares the value of the When Created attribute to the values of the following attributes:
- Last-Logon-Timestamp
- Password Last Set
Also, Adaxes tries to ping the computers that appear to be inactive for a long time based on the attributes.